Wedoany.com Report-Aug. 28, The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) has extended the duration of nuclear power plant design certifications from 15 years to 40 years, effective September 15, 2025. This change applies to designs by companies including GE Vernova Hitachi Nuclear Energy, NuScale Power, Westinghouse Electric Company, and a Korean consortium, with Westinghouse’s AP1000 certification now valid until 2046.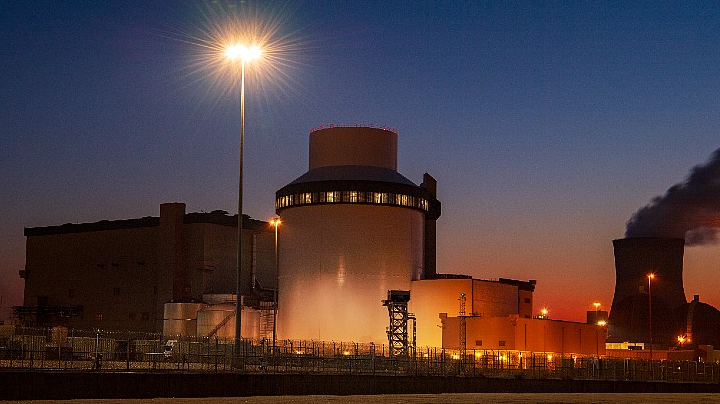
Vogtle 3 and 4 are new AP1000 units
The NRC stated: “This change maintains our focus on safety with less regulatory effort and gives designers more time to gather operating experience before asking to renew a certification.” Design certifications confirm that a nuclear power plant’s generic design meets U.S. safety and regulatory standards, streamlining the approval process for new projects, though site-specific permits are still required.
The AP1000, originally certified in 2006, benefits significantly from this extension, simplifying the licensing process for new units in the United States. Dan Lipman, President of Westinghouse Energy Systems, noted: “The expansion of the AP1000 design certification to 40 years further positions the advanced AP1000 modular reactor as the leading solution to meet the bold vision of the US to have 10 large-scale reactors under construction by 2030. In addition, the extension establishes a long-term licensing path to deploy our AP1000 technology abroad by providing international regulators with an established design that has already met rigorous safety standards.”
The NRC’s certified designs include the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR) by GE Nuclear Energy, the Advanced Power Reactor 1400 (APR1400) by Korea Electric Power Corporation and Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power, the System 80+ and Advanced Passive 600 (AP600) by Westinghouse, the Economic Simplified Boiling-Water Reactor (ESBWR) by GE-Hitachi Nuclear Energy, and the NuScale Small Modular Reactor (US600) by NuScale Power, alongside the AP1000.
This extension provides reactor designers and operators with greater flexibility to leverage certified designs over an extended period, reducing regulatory burdens while maintaining safety standards. It supports the U.S. goal of expanding nuclear energy capacity, enhancing energy reliability, and promoting sustainable power solutions.
The prolonged certification period also facilitates international adoption of these designs, as global regulators can reference the NRC’s rigorous safety evaluations. This development is expected to accelerate the deployment of advanced nuclear technologies, contributing to both domestic and global energy needs while prioritizing safety and efficiency.


























 京公网安备 11010802046720号
京公网安备 11010802046720号